It’s time to make corporate communication services available remotely with no additional efforts like using Cisco Anyconnect and/or creating VPN tunnels.
In this article, we’ll tell you how to configure Cisco Expressway server to make videoconferencing work from outside your office as well.

Cisco Expressway provides a secure firewall for voice and video sharing, and supports many features, such as B2B calls, mobile and remote access (MRA), and also TURN server capabilities (Traversal Using Relay NAT). So, this can be called a Single Edge solution which is a preferable borderline solution for unified communications and Cisco Meeting Server.
Licensing
 Cisco Expressway servers can be deployed as Core (Expressway-C) and Edge (Expressway-E). If they are being deployed from scratch, they are not Expressways at first, they are simply VCS servers. You must install the required licenses to make them Expressway servers.
Cisco Expressway servers can be deployed as Core (Expressway-C) and Edge (Expressway-E). If they are being deployed from scratch, they are not Expressways at first, they are simply VCS servers. You must install the required licenses to make them Expressway servers.
Each server (no matter Edge or Core) requires a LIC-SW-EXP-K9 license (to put it simple, a Release key).
Core servers require the following licenses:
- LIC-EXP-GW
- LIC-EXP-SERIES
Edge servers require the following licenses:
- LIC-EXP-GW
- LIC-EXP-SERIES
- LIC-EXP-E
- LIC-EXP-TURN
Optionally, you can add the following licenses:
- LIC-EXP-MSFT-PMP — Microsoft Interoperability Option (for Expressway-C), it is required for interactions with Skype for Business;
- LIC-EXP-RMS-PMP — Rich Media Session licenses (for both Expressway-C and Expressway-Е);
- LIC-EXP-DSK — Expressway Desktop Endpoint license (for Expressway-C), to register personal endpoints to Expressway;
- LIC-EXP-ROOM — Expressway ROOM license (to register video codecs to Expressway);
- LIC-TP-ROOM — to register codecs to CUCM (optionally includes LIC-EXP-ROOM);
- LIC-EXP-AN — Advanced Networking option, an additional network interface (for both Expressway-C and Expressway-Е)
Rich Media Session license consumption depends on the connection type:
- Connections to/from Expressway Registered Endpoints;
- Connections to/from Expressway Non-Registered Endpoints;
- Connections to/from through Traversal Zone;
- Connections to/from Cisco Cloud Service;
- Connections to/from UCM, Conductor, CMS or Expressway through Neighbor Zone.
In my case, the virtual machines have been already deployed and network interfaces have been configured.
Looking forward, there are different scenarios of Expressway-C and Expressway-E bundle deployment.
In terms of domains, there are two options:
1. Single domain (if you have a single domain, e.g. example.com, to be used both inside and outside your network).
2. Dual domain (internal domain is example.local, external domain is example.com).
In terms of topology, it’s recommended to use two network interfaces, one for each separate DMZ. However, we’ll consider two options:
1. DMZ with a single local network interface for Expressway-E.
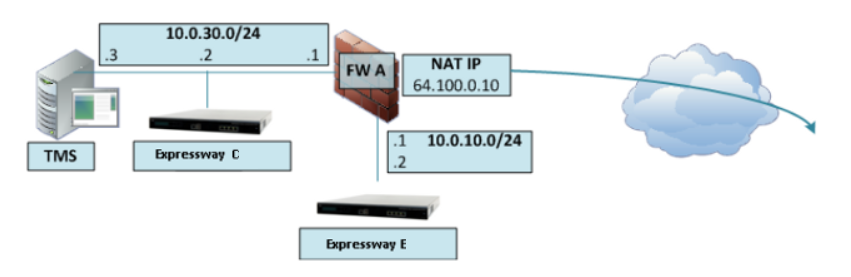
You can use a public IP address given by your internet provider. No need to configure NAT Reflection at your firewall to make Cisco Meeting Server work outside your network.
2. DMZ with two local network interfaces for Expressway-E.
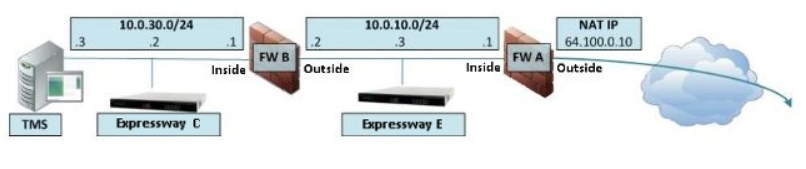
To use this feature, you should have Advanced Networking option active in Option keys section.
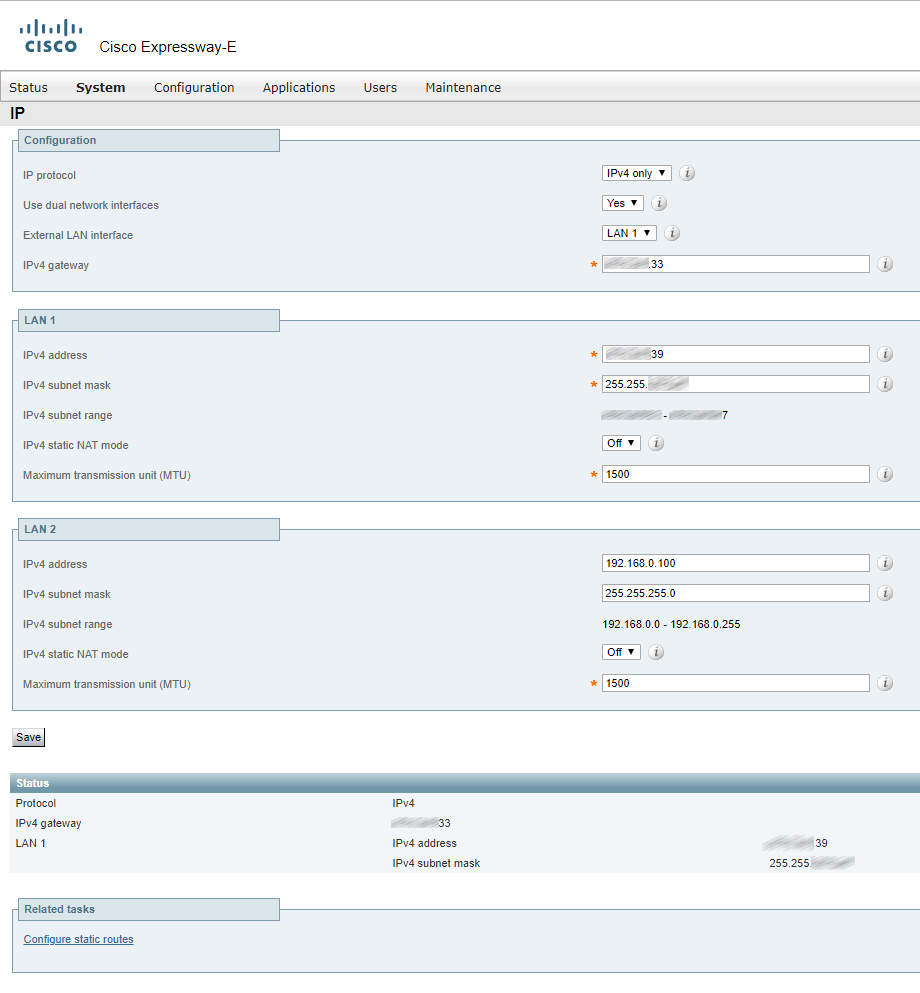
Besides, in both cases you have to specify whether this IP address will be visible from outside the NAT.
DNS
You should create the following external/internal DNS records (depending on whether you are deploying a clustered or non-clustered, Single or Dual Domain server):
Single Domain
| DNS | TYPE | Record | Purpose |
| External | A | exp-e. external-example.com | Expressway-E internet address. You can use any other name. |
| External | A | join. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for connecting to CMS conference via WebRTC. |
| External | SRV | _collab-edge._tls. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for telephony, messenger and voice mail services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| External | SRV | _sip._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for incoming calls. Port 5060. |
| External | SRV | _sip._udp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for incoming calls. Port 5060. |
| External | SRV | _sips._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for encrypted incoming calls. Port 5061. |
| Internal | SRV | _cisco-uds._tcp. internal-example.com | Points to Cisco UCM’s A record. Required for telephony services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _cuplogin._tcp. internal-example.com | Points to Cisco UP’s A record. Required for messenger services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _xmpp-client._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco Meeting Server’s A record. Required for clients to find XMPP server. |
| Internal | SRV | _xmpp-server._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco Meeting Server’s A record. Required for CallBridges to find XMPP server. |
Dual Domain
| DNS | TYPE | Record | Purpose |
| External | A | exp-e. external-example.com | Expressway-E internet address. You can use any other name. |
| External | A | join. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for connecting to CMS conference via WebRTC. |
| External | SRV | _collab-edge._tls. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for telephony, messenger and voice mail services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| External | SRV | _sip._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for incoming calls. Port 5060. |
| External | SRV | _sip._udp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for incoming calls. Port 5060. |
| External | SRV | _sips._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Expressway-E address. Required for encrypted incoming calls. Port 5061. |
| Internal | SRV | _cisco-uds._tcp. internal-example.com | Points to Cisco UCM’s A record. Required for telephony services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _cisco-uds._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco UCM’s A record. Required for telephony services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _cuplogin._tcp. internal-example.com | Points to Cisco UP’s A record. Required for messenger services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _cuplogin._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco UP’s A record. Required for messenger services to be discovered by Jabber client app. Port 8443. |
| Internal | SRV | _xmpp-client._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco Meeting Server’s A record. Required for clients to find XMPP server. |
| Internal | SRV | _xmpp-server._tcp. external-example.com | Points to Cisco Meeting Server’s A record. Required for CallBridges to find XMPP server. |
Please note that if you have a Dual Domain server, you should create a zone with an external domain in your internal DNS, and then create the red-marked records in it. So, the users will be able to use the same login for their Cisco Jabber apps, whether they are logging in from inside or outside the corporate network (with an external domain, login names usually coincide with corporate email addresses).
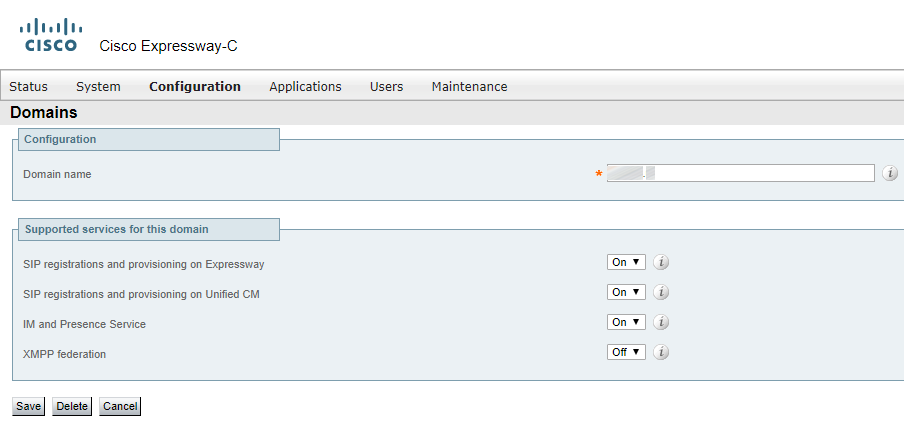
You should also create domains and select the services to be supported for this domains.
Services
- SIP registrations and provisioning on Expressway — indicates if Expressway is trusted for this SIP domain. Expressway acts as a SIP registrar and presence server for this domain, and also accepts registration requests from all SIP clients trying to register with an alias that includes this domain.
- SIP registrations and provisioning on Unified CM — indicates if Expressway acts as a gateway for CUCM to provide safe pass through a firewall and support endpoint registration to CUCM.
- IM and Presence Service — indicates if Expressway acts as a gateway for IMP and supports messenger and presence services.
- XMPP federation — for a local domain that requires XMPP federation services (a domain that participates in federation with any other domains).
Please note that if you need static routes for federated external domains, they should be configured on Expressway-E.
If you are using Dual Domain scenario, you should enter both domain names in Expressway-C and Expressway-E configuration sections (or all domain names, if there are more than two of them).
In the next part of this article, we’ll go on with Expressway configuration (specifically, we’ll talk about certificates and zones).
Read also:
- Part 1 - Cisco Expressway 12.5.5. Remote Videoconferencing without VPN
- Part 2 - Cisco Expressway 12.5.5. Remote Videoconferencing without VPN
- Part 3 - Cisco Expressway 12.5.5. Remote Videoconferencing without VPN
