- Part 1 – Prerequisites
- Part 2 – the VIS role
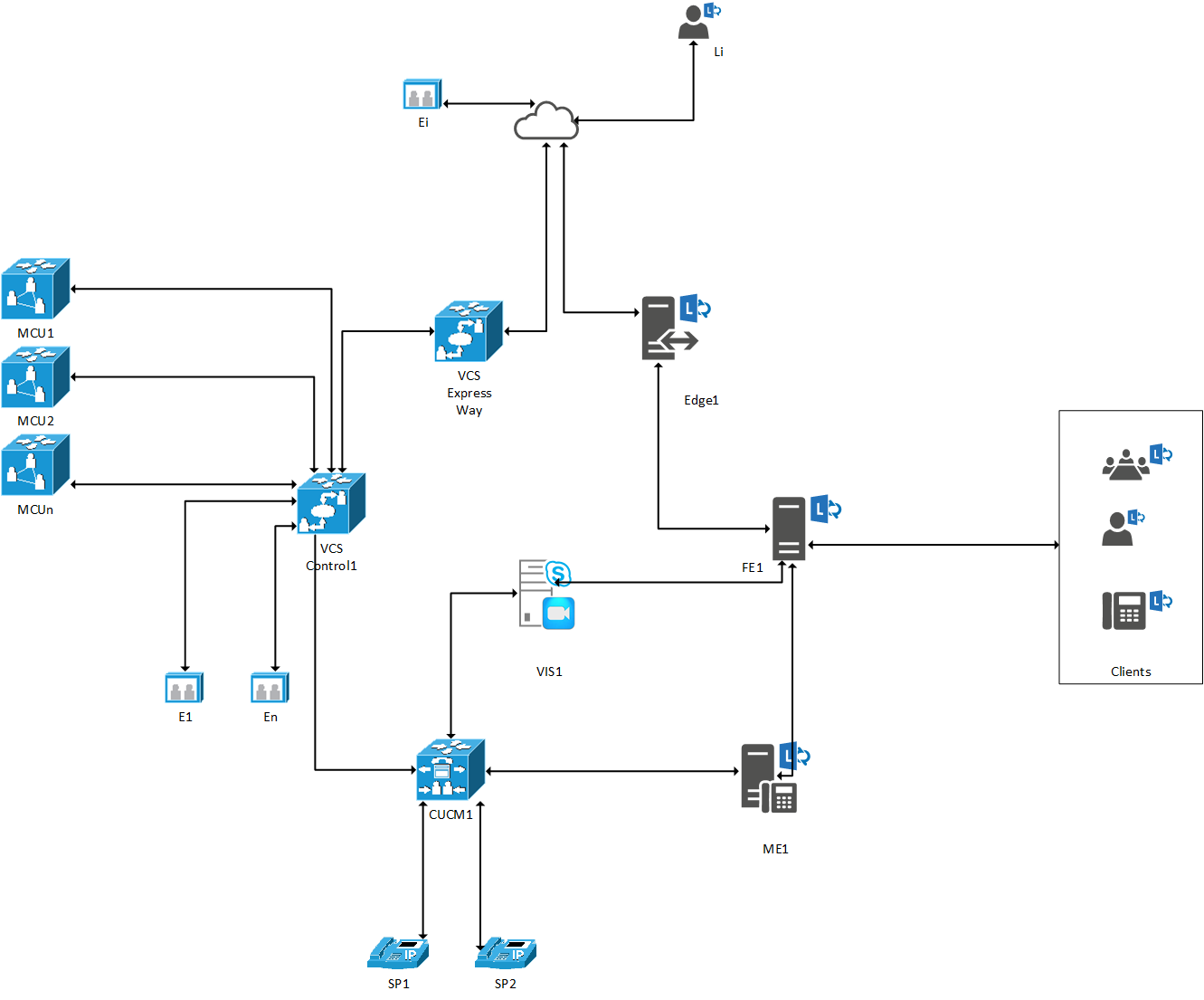
- Part 3 – CUCM Configuration
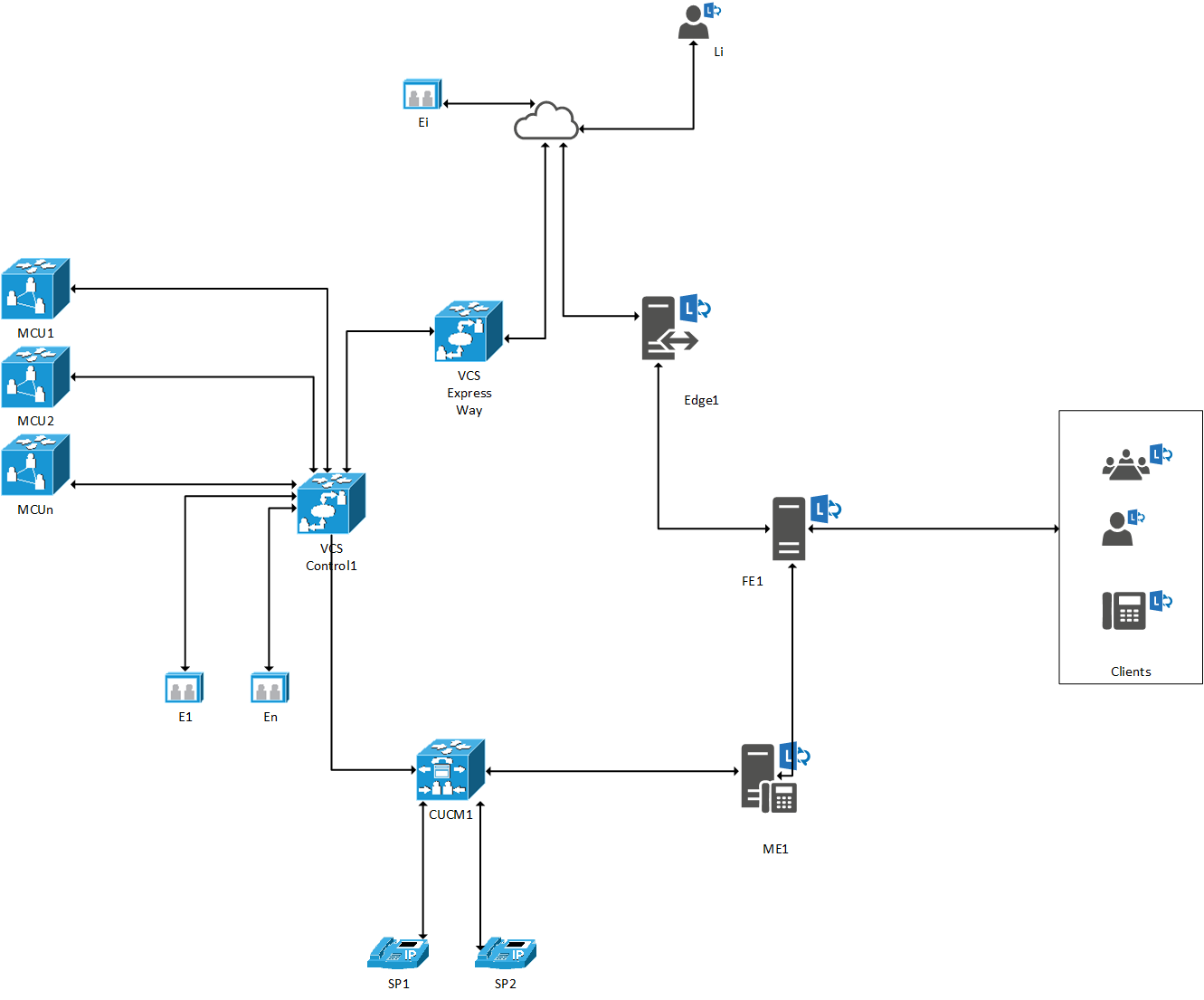
The CUCM configuration consists of two parts: creating a trunk to VCS Control and a trunk the VIS.
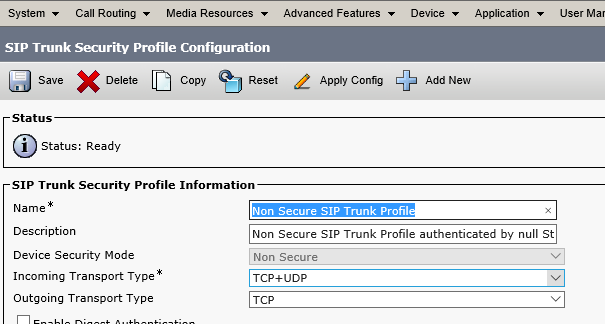
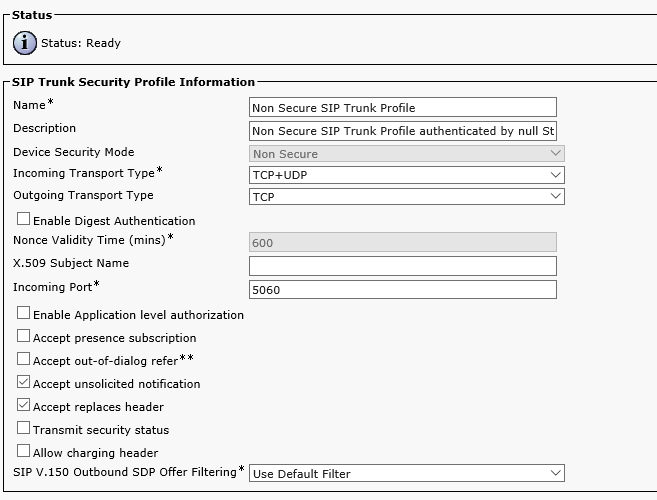
In CUCM proceed to CM Administration->System->Security->SIP Trunk Security Profile, select "Non Secure SIP Trunk Profile", and click Copy.
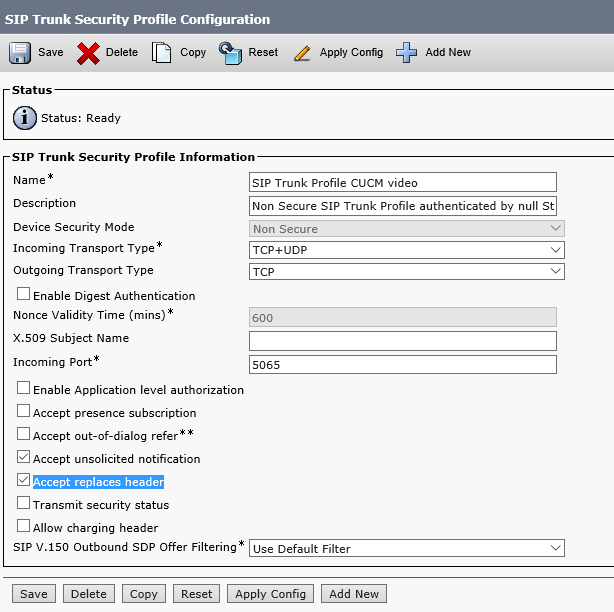
Enter the name for the new trunk, for example 'SIP Trunk Profile CUCM video', set the Incoming Port to 5065, check 'Accept unsolicited notification' and 'Accept replaces header', and click Save.
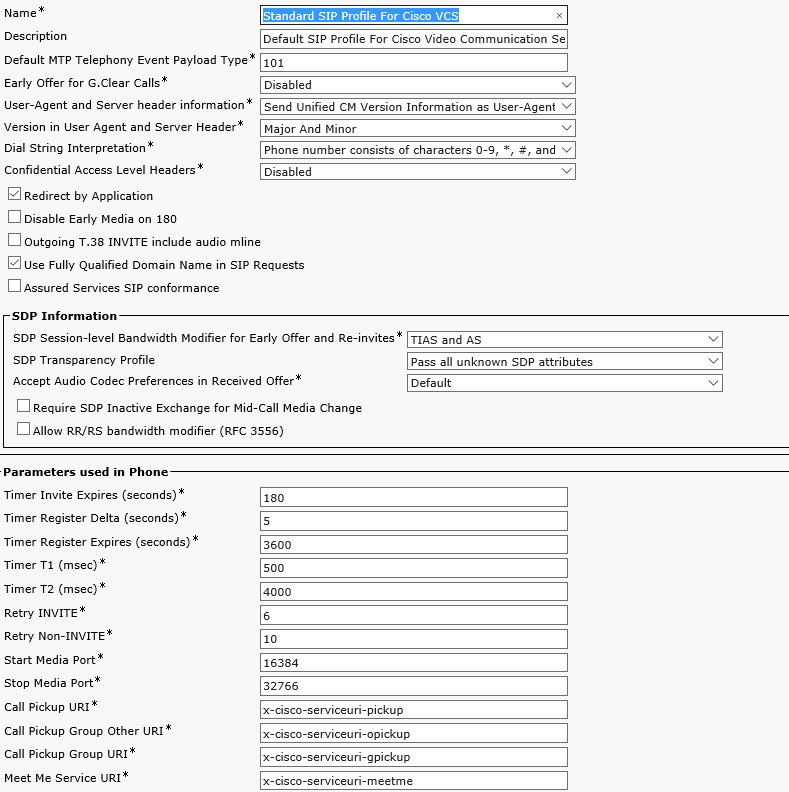
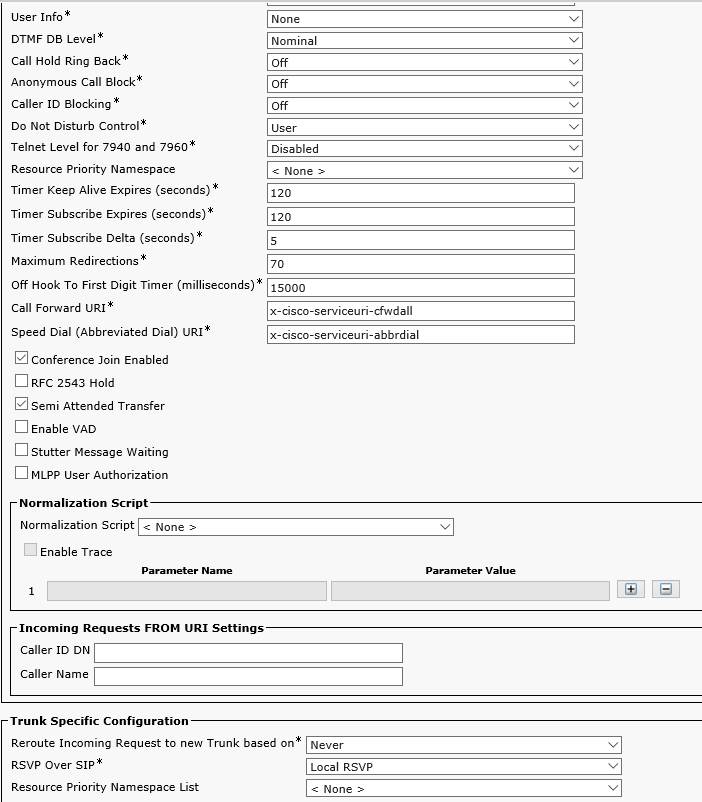
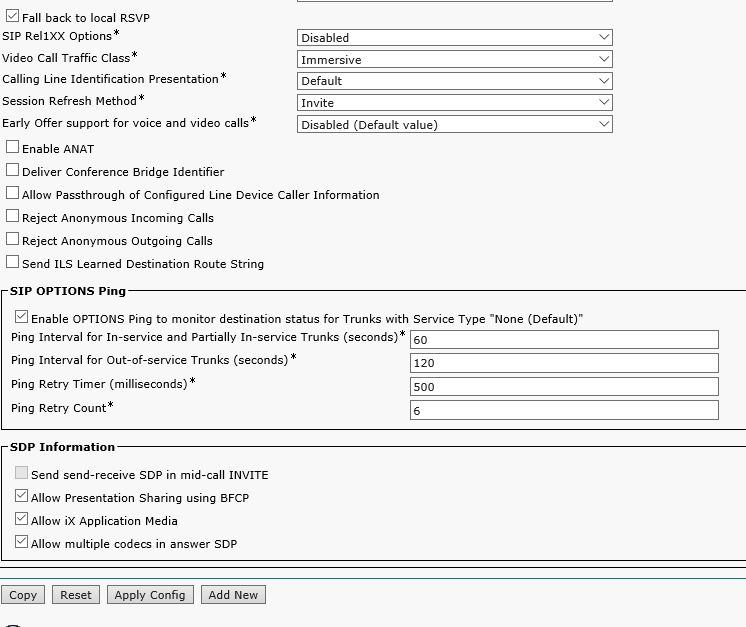
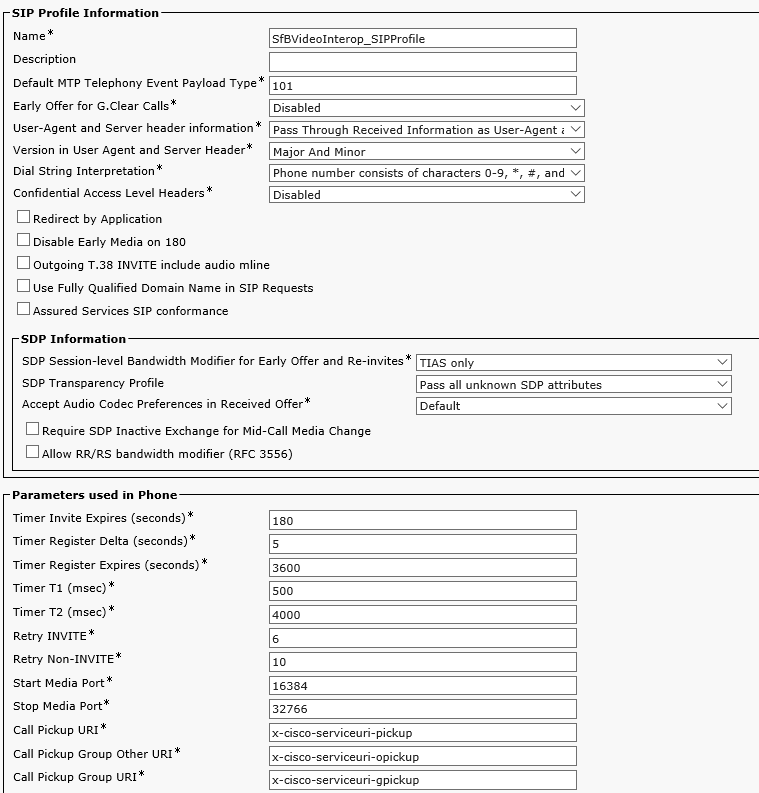
Now proceed to Device-> Device Settings-> SIP Profile and configure the Standard SIP Profile For Cisco VCS as the screenshot shows. Depending on the CUCM version this profile may have different parameters.
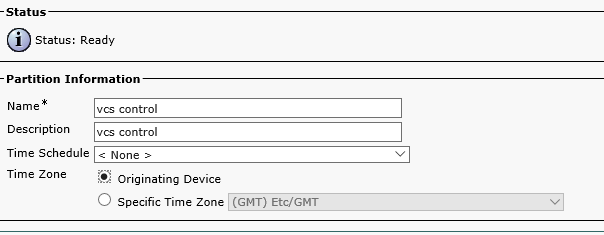
Create a partition for VCS Control: Call Routing->Class of Control->Partition
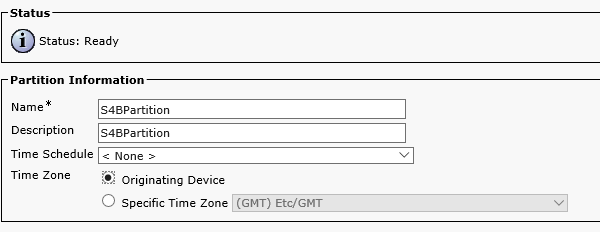
And for S4B:
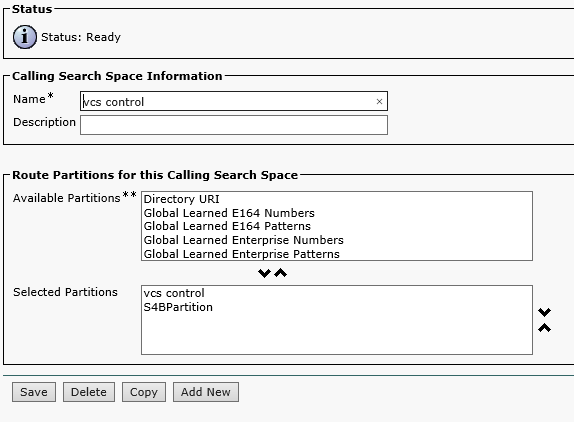
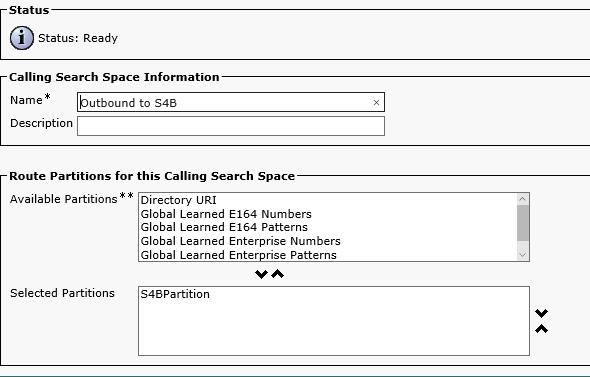
Create a Calling Search Space: Call Routing->Class of Control->Calling Search Space:
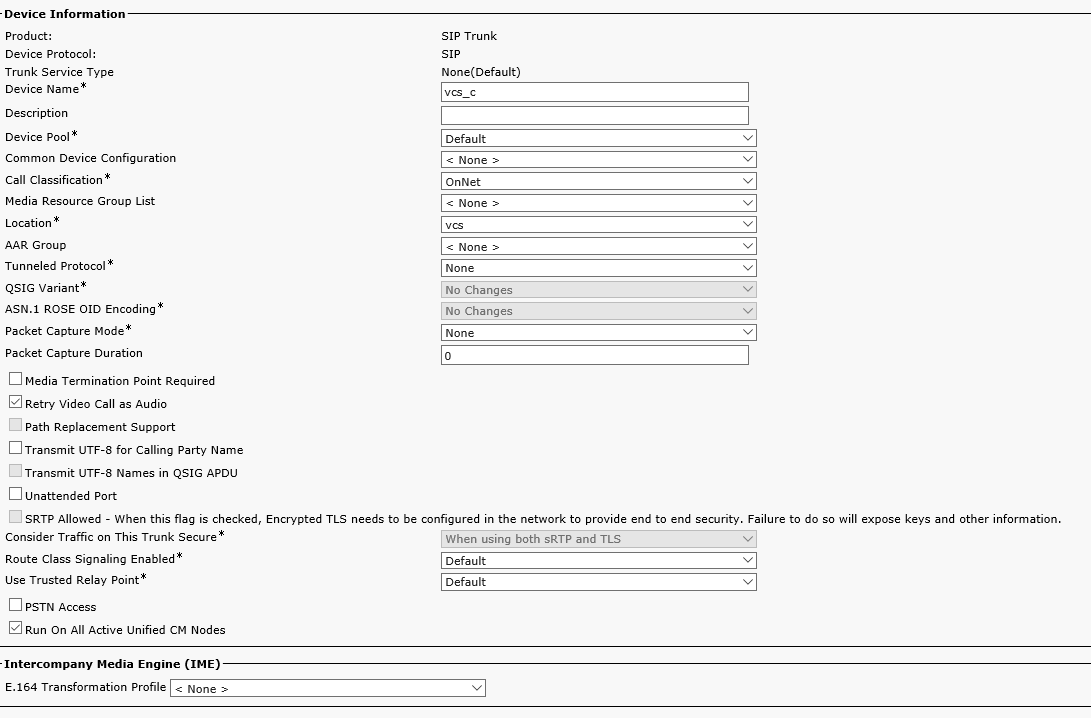
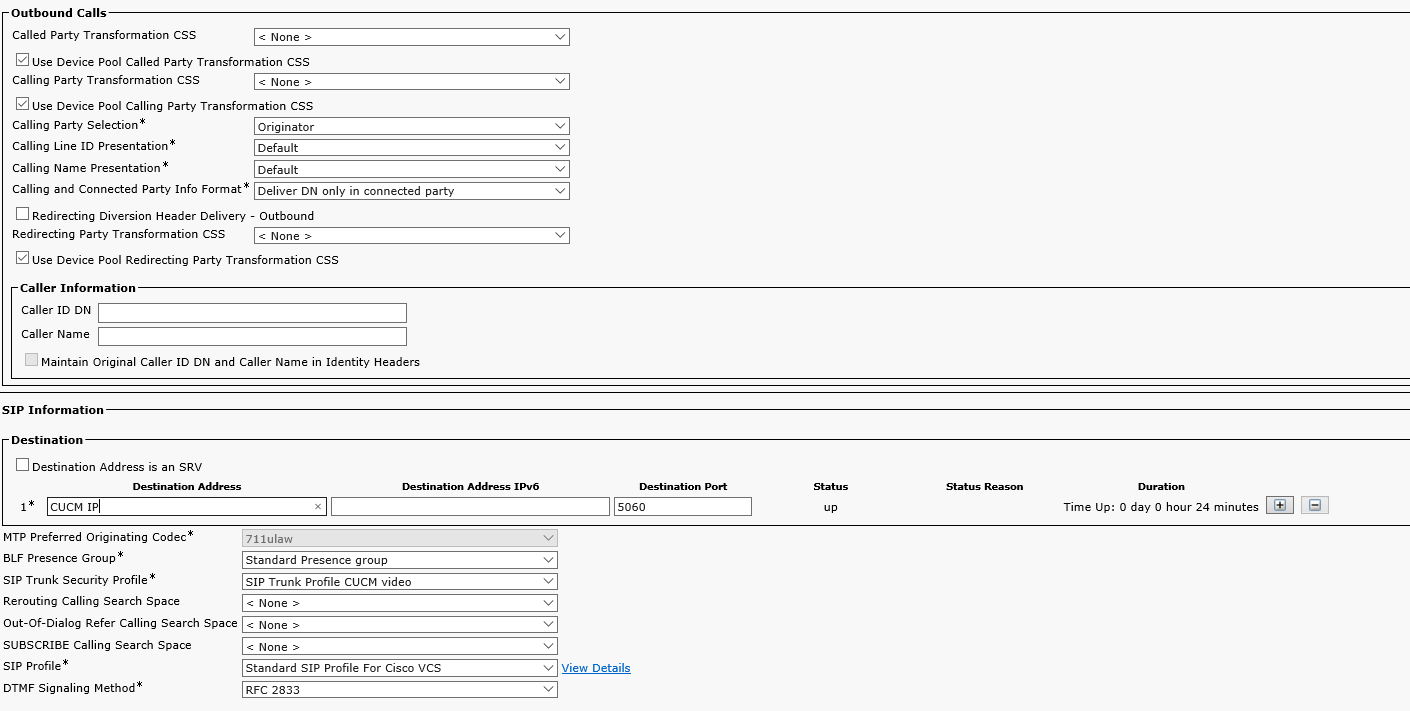
Create a new trunk: Device -> Trunk. Replace 'CUCM IP' with your VCS Control IP address.
After you save the trunk settings, click Reset.
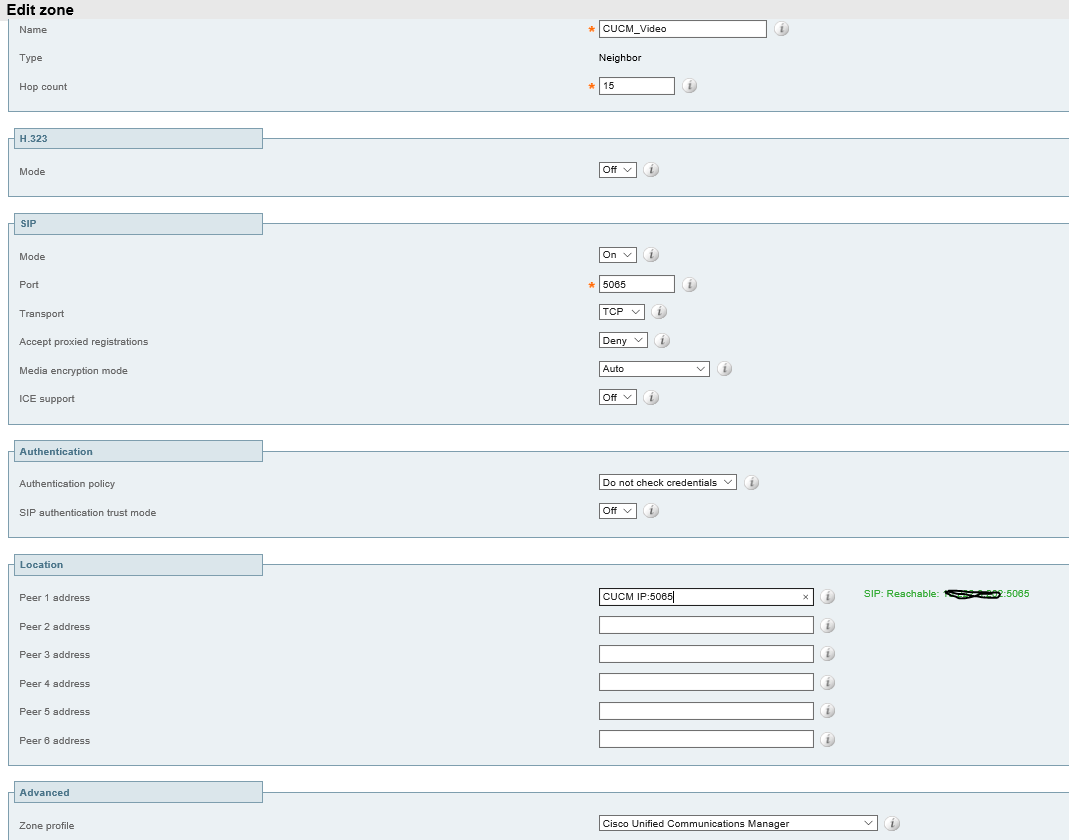
Then proceed to VCS Control Configuration->Zones to create a new zone.
Replace 'CUCMIP' with your CUCM IP address.
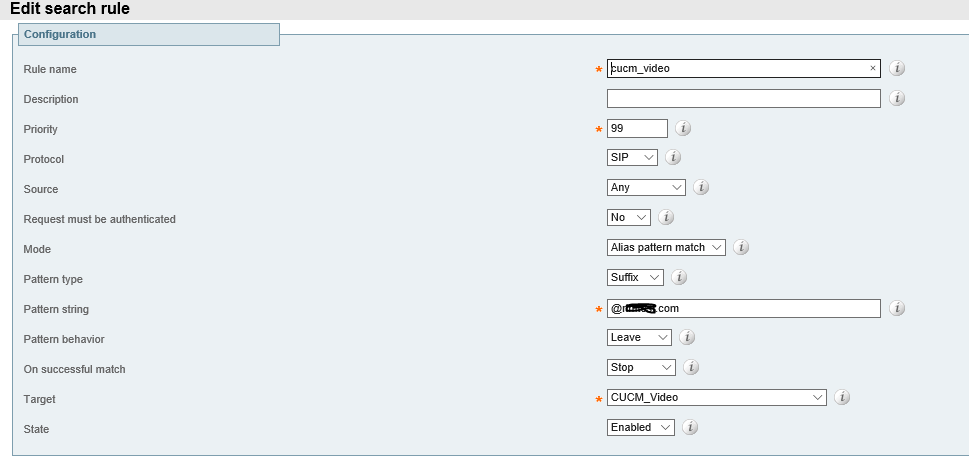
Save the form, create a Dial Plan for calling S4B users. In this case, the domain name suffix is used as a pattern. This rule is configured in such way that if a user user1@test.com is dialed, the CUCM Video trunk is used. You can use a regular expression as a pattern.
Configuration->Dial Plans-> Search Rules
The trunk between the CUCM and VCS Control is configured, now configure the trunk between the CUCM and S4B.
Create a new Calling Search Space: Call Routing->Class of Control->Calling Search Space
Create a security profile: SIP System->Security->SIP Trunk Security Profile
Create a SIP Profile: Device->Device Settings->SIP Profile
After you save the form, click Reset.
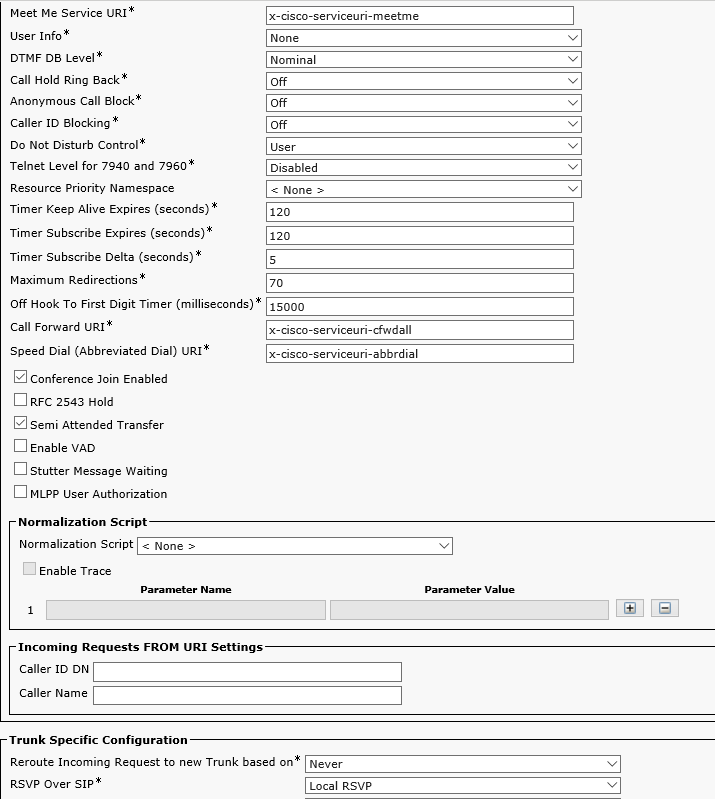
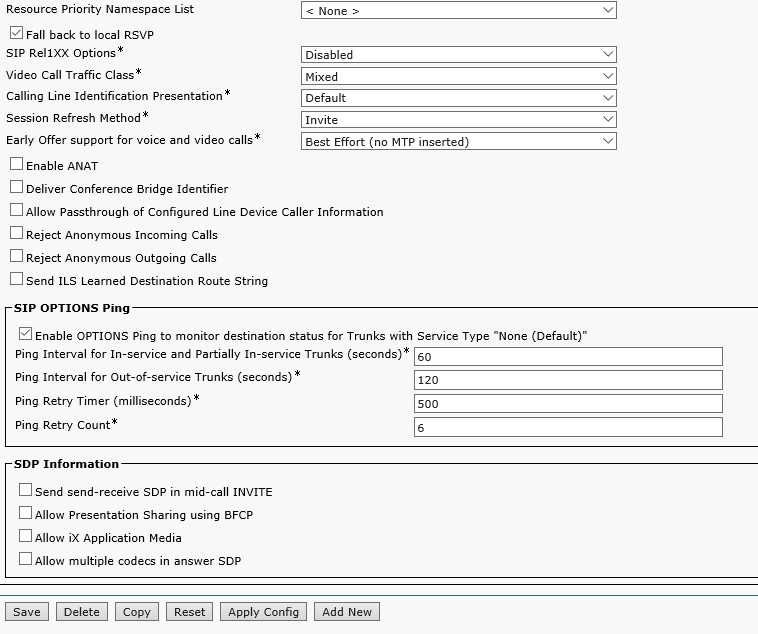
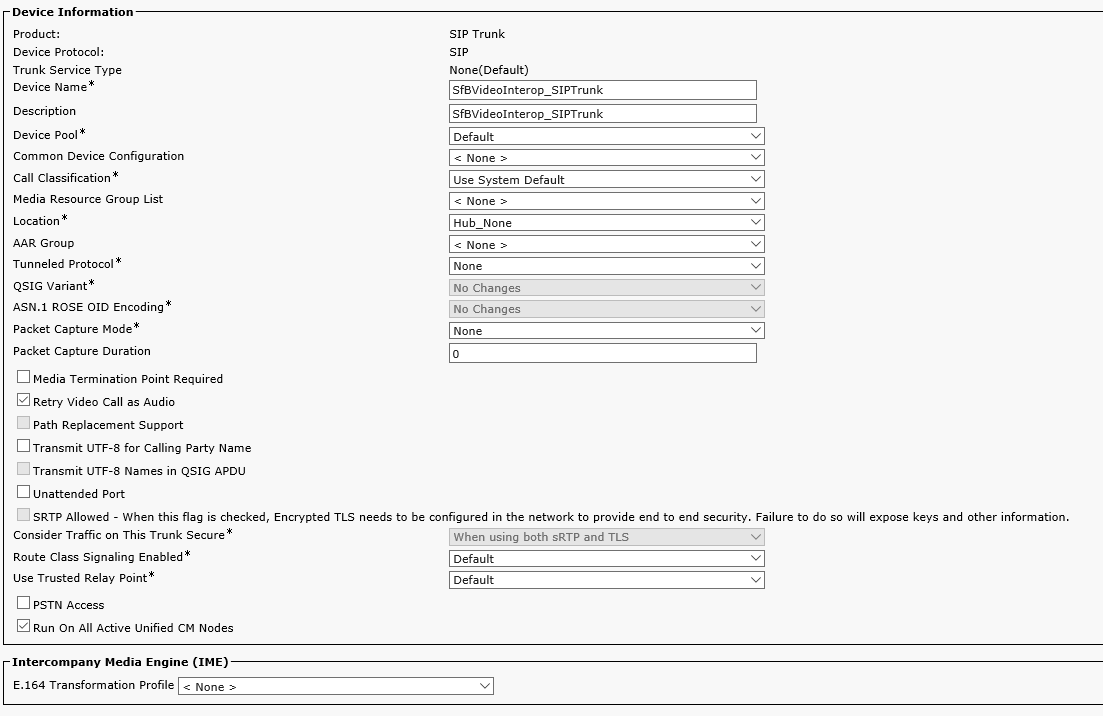
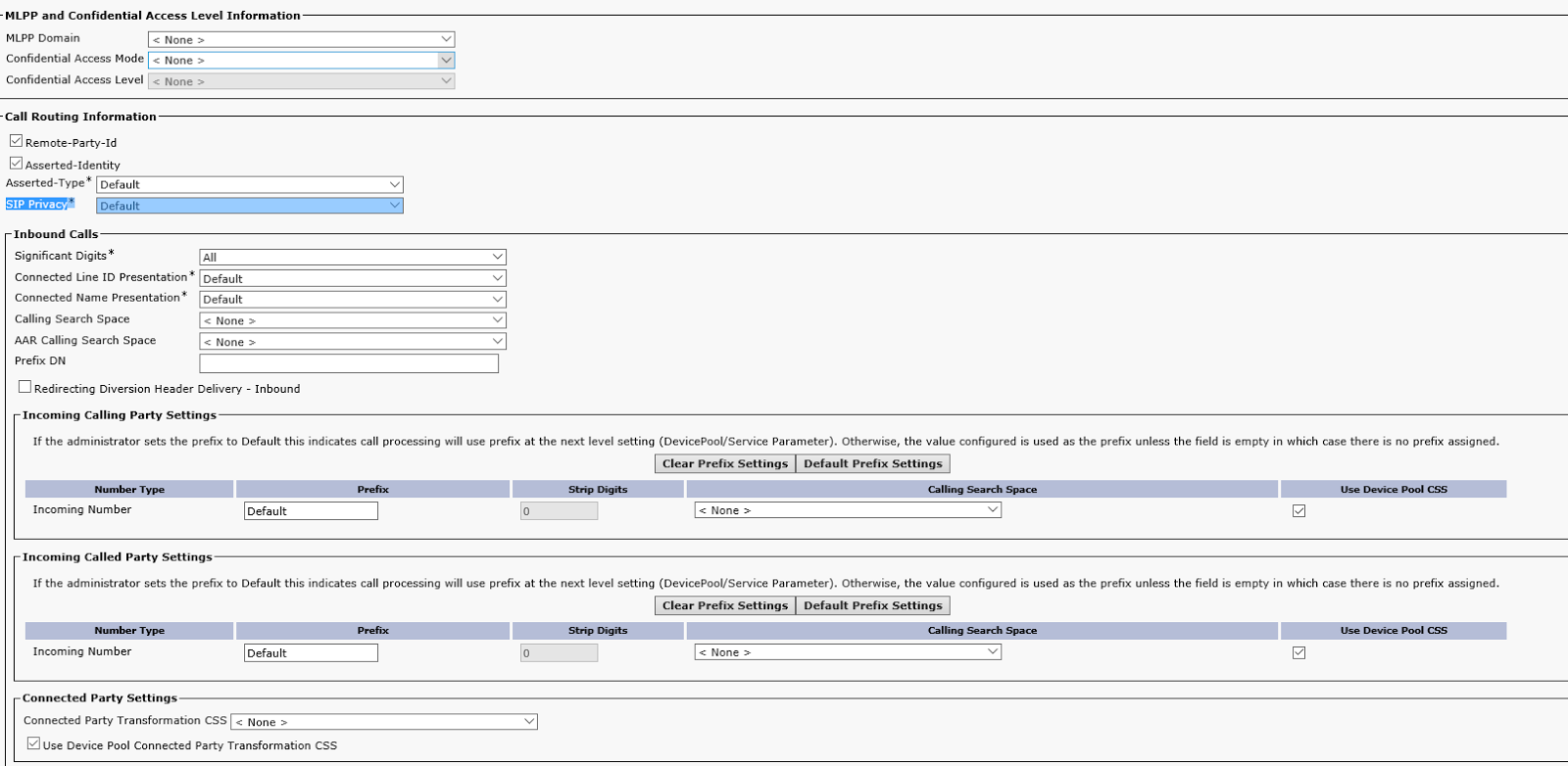
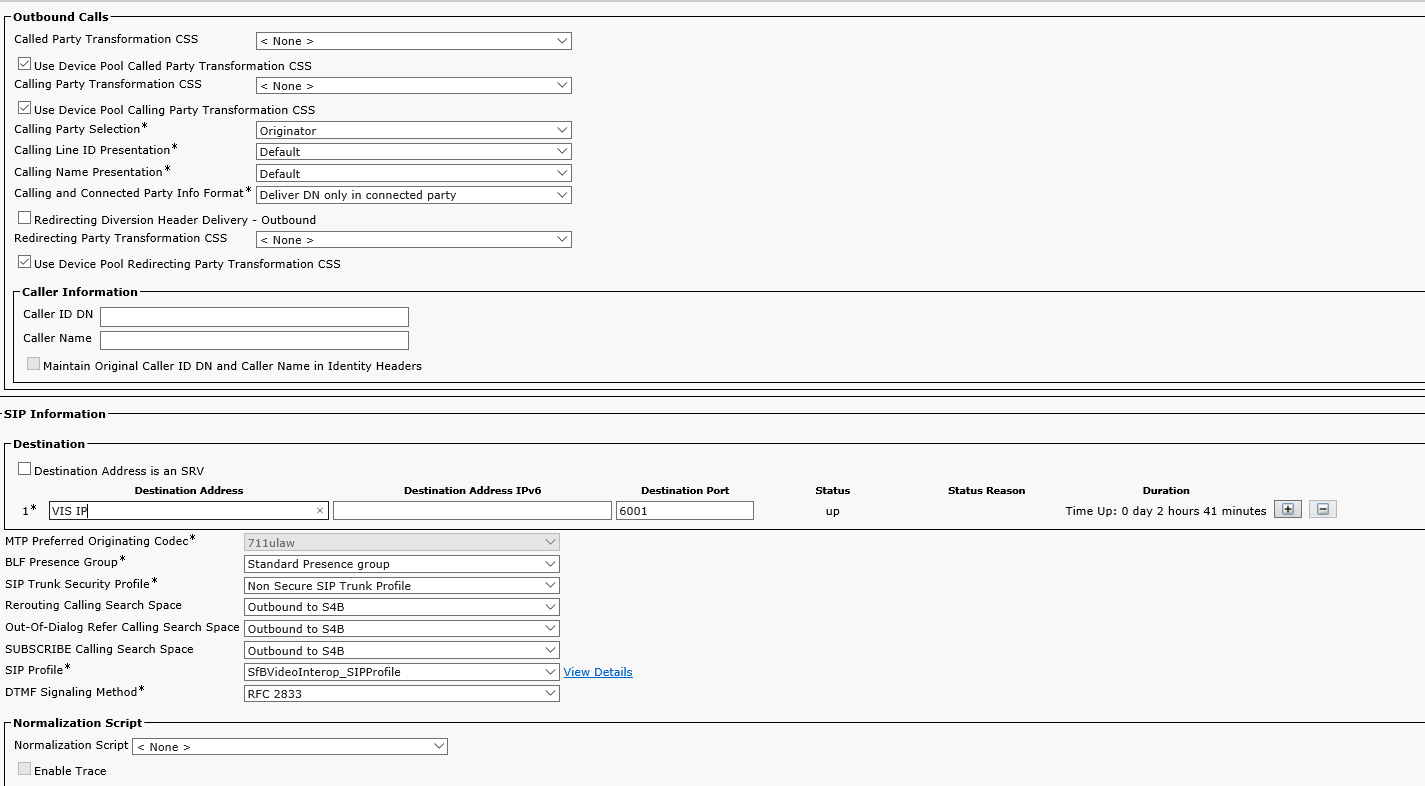
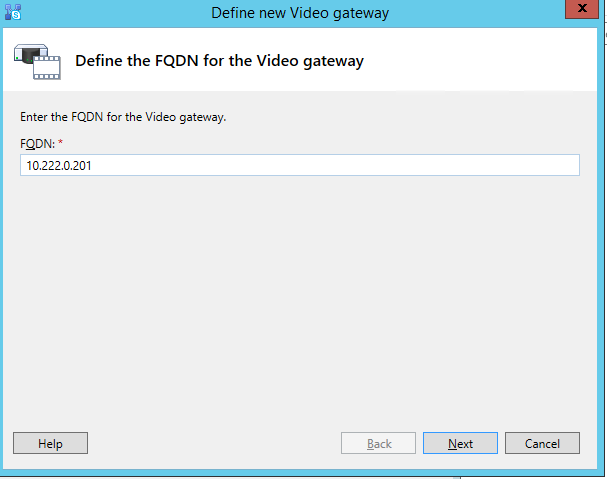
Create a trunk to VIS: Device->Trunk, replace 'VIS IP' with the VIS IP address
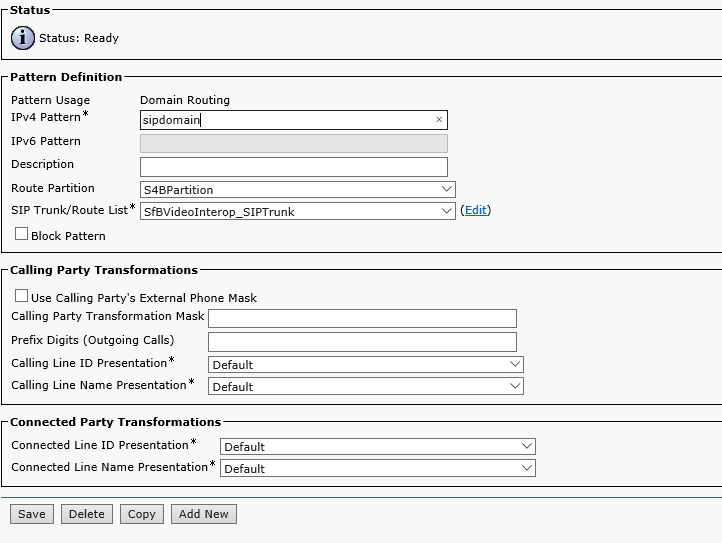
Create a pattern for sending calls to the S4B trunk. It is important to specify the IPv4 pattern: you should give the full domain name, for example, domain1.com, and also select the Route Partition and SIP Trunk.
Proceed to Call Routing->SIP Route Pattern and enter your SIP domain
That's it. It's time to test.